| Sr. No. |
FEATURES |
MERITS |
| A |
FURNACE WALL |
| |
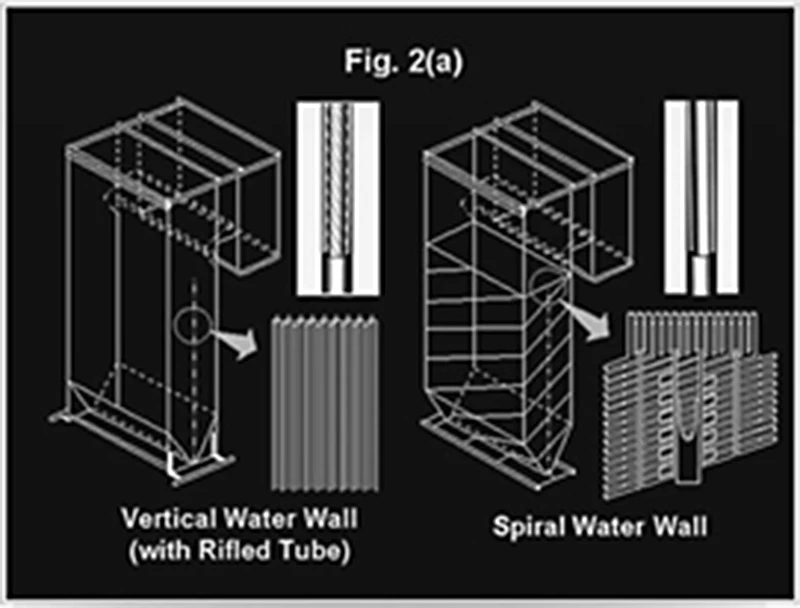
- Vertical wall construction as standard
- MHI has largest number of sliding pressure vertical wall supercritical units in operation
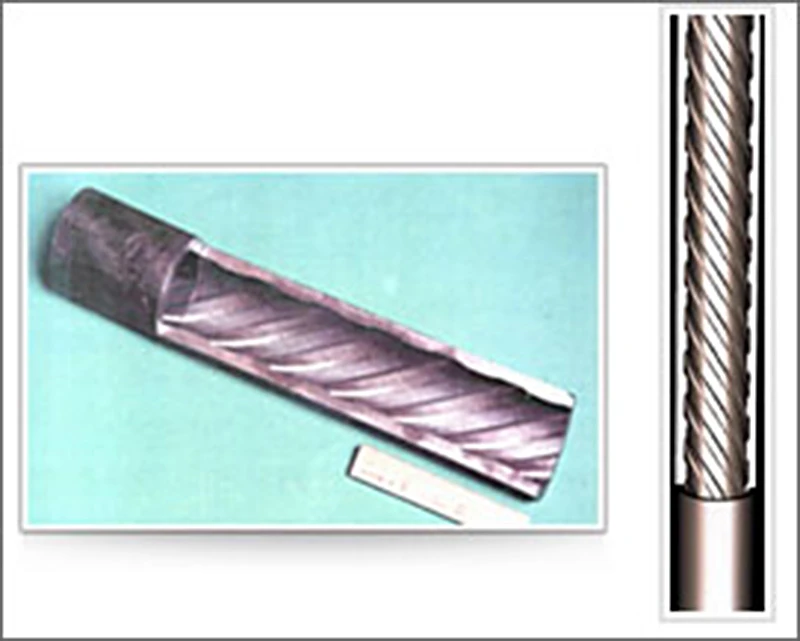
- Rifled tube construction In high heat flux zone
|
- Easier manufacturing and simpler construction
- Low mass flux compared to spiral wall and hence lesser pressure drop
- Lesser field joints
- Less slag accumulation
- Less thermal stresses
- Simpler supporting arrangement
|
| |
 |
 |
| B |
FIRING ARRANGEMENT |
| |
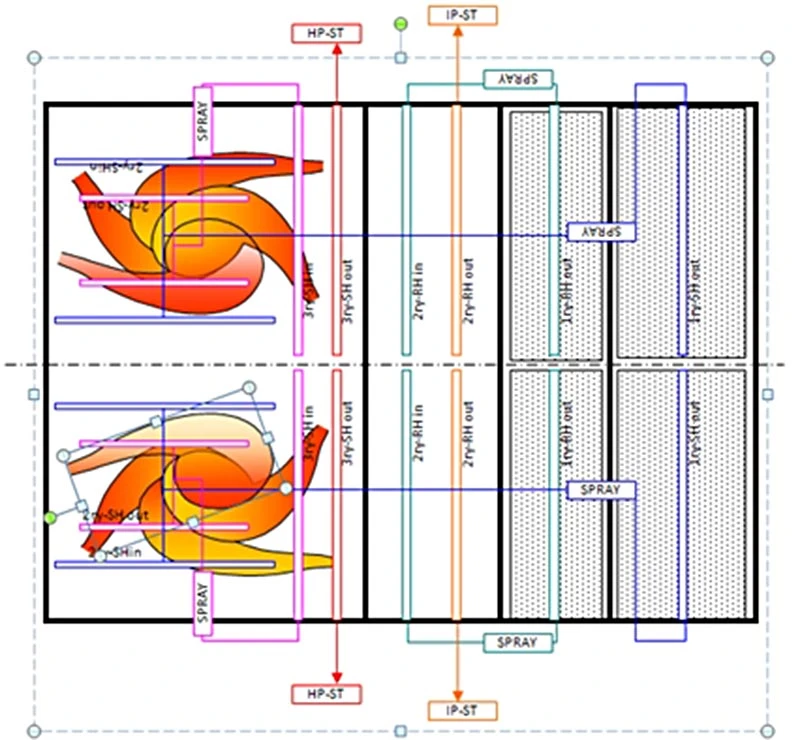
Circular corner firing (CCF) with twin fire vortex as standard |
- Less steam temperature imbalance between left and right leads
- Uniform heat flux in the furnace
- Less burner heat input
|
| |
 |
| C |
COAL FIRING SYSTEM |
| |
Use of MACT (Mitsubishi Advanced Combustion Technology) with APM (Advanced Pollution Minimum) burner and additional air port |
- High ignition ability under low O2 condition
- Reduced NOx emmisions
- Reduced unburn carbon loss
- Low excess air (15%) increases boiler efficiency
|
| D |
R H TEMPERATURE CONTROL |
| |
- Use of gas biasing damper in the second pass as primary control
- Additional tilting mechanism for burners as a secondary control
- Interstage attemperation as emergency control
|
- Pressure control of RH temperature is achieved
- No RH spray under steady state operation
|
| E |
SUPERHEATER CONFIGURATION |
| |
- Use of three stage superheater
- Use of inter stage attemperation
|
Better SH steam temperature control |
| F |
USE OF ADVANCED RELIABLE MATERIALS FOR HIGH TEMPERATURE APPLICATIONS |
| |
- CC2328 (SA213 UNS S30432) in SH & RH applications
- Above material has been devloped by MHI in collaboration with tube manufacturers for supercritical and ultra supercritical boilers
- Non-usage of T91 materials in heating zone
|
- Better creep properties
- Reduced steam oxidation leading to higher availability as compared to T91 materials
|


